Setup EBS Volume
What is AWS EBS?

Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) is a block storage service provided by AWS, designed to be used with EC2 virtual machines. Each EBS volume operates similarly to an external hard drive: it can be attached to an EC2 instance and used to store data such as operating systems, files, databases, etc.
In the Kubernetes context, EBS is used as a Persistent Volume (PV) — meaning a long-term storage area that doesn’t get lost when Pods are deleted or Nodes are restarted. This is very important for applications that need to store state (stateful applications) such as databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Redis…), content management systems, or file processing systems.
Why use EBS in Kubernetes? - Automatically provision and attach volumes to Pods through PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC). - Persistent storage — data remains after Pods or Nodes are destroyed or restarted. - High performance, low latency — suitable for applications requiring fast access speed. - Good integration with EKS — developed and directly supported by AWS.
What is EBS CSI Driver?
In Kubernetes, to connect and manage EBS volumes, you need a driver called: EBS CSI Driver (Container Storage Interface Driver)
This is an intermediary component that helps Kubernetes communicate with AWS’s EBS service. EBS CSI Driver is responsible for:
- Automatically creating EBS volumes when PVC is created
- Attaching volumes to the Node where the Pod is running
- Removing or deleting volumes when no longer in use
When a Pod requests storage through PVC, Kubernetes will rely on the CSI Driver to perform actual operations with AWS’s EBS service.
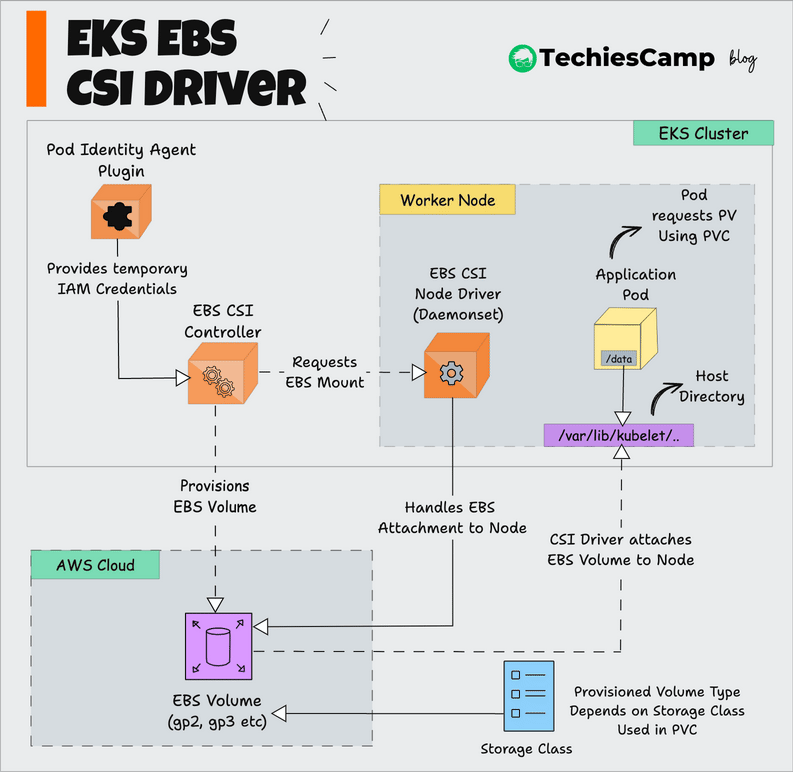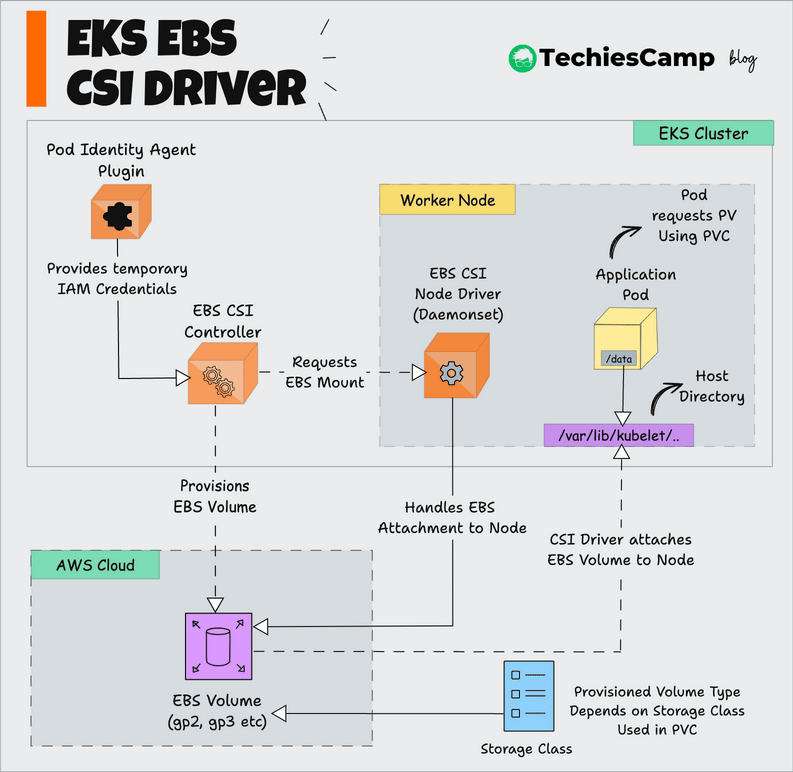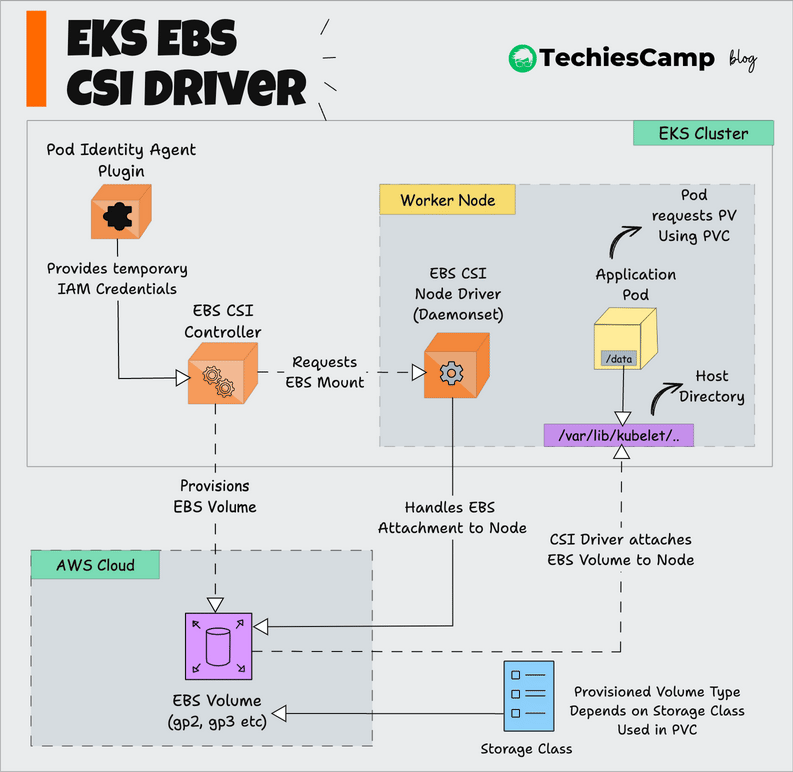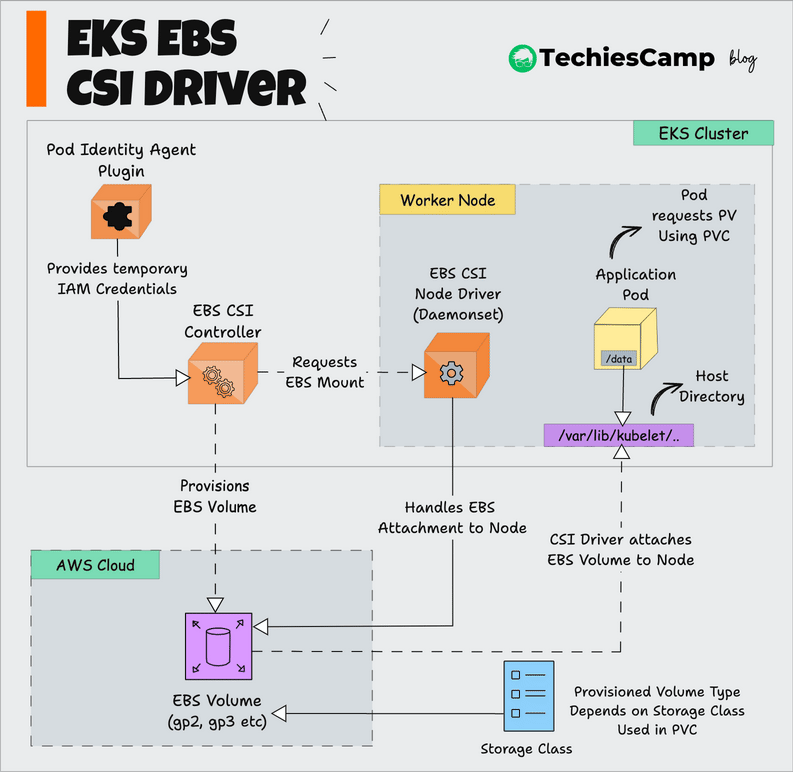 Source: Techies Camp
Source: Techies Camp
Diagram explanation:
Pod sends storage request via PersistentVolumeClaim.
Kubernetes API Server receives the request and forwards it to EBS CSI Driver.
CSI Driver sends command to AWS to create a corresponding EBS Volume.
Volume is attached to the Node where the Pod runs.
Pod can read/write data directly to the EBS Volume like a disk drive.
Install EBS CSI Driver
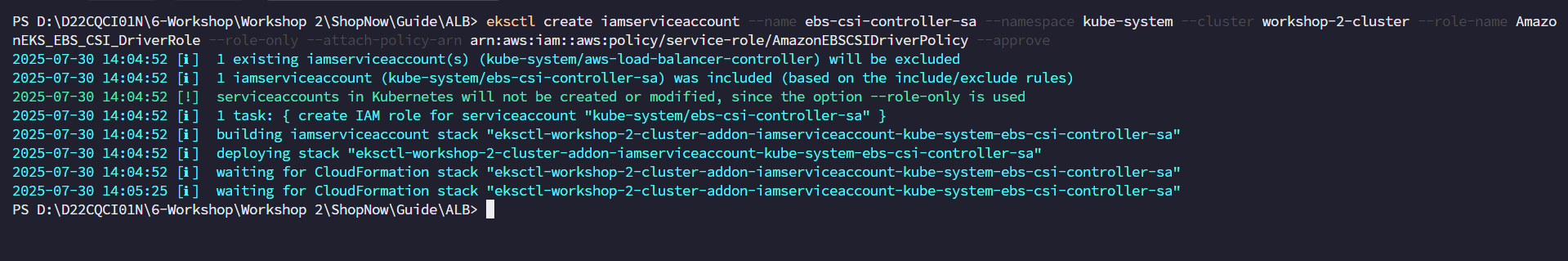
Create IAM Service Account
eksctl create iamserviceaccount \ --name ebs-csi-controller-sa \ --namespace kube-system \ --cluster workshop-2-cluster \ --role-name AmazonEKS_EBS_CSI_DriverRole \ --role-only \ --attach-policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AmazonEBSCSIDriverPolicy \ --approve
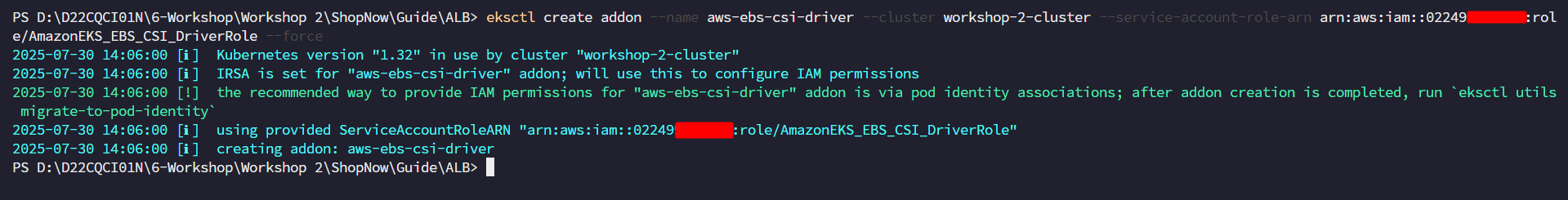
Install EBS CSI Driver, replace
<account_id>with your account ID.eksctl create addon --name aws-ebs-csi-driver --cluster workshop-2-cluster --service-account-role-arn arn:aws:iam::<account_id>:role/AmazonEKS_EBS_CSI_DriverRole --force
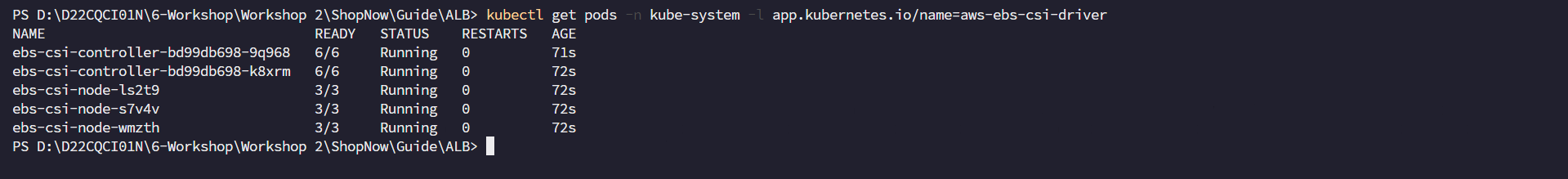
Check installation
kubectl get pods -n kube-system -l app.kubernetes.io/name=aws-ebs-csi-driver