Create ECR Repository and EKS Cluster
ECR Repository
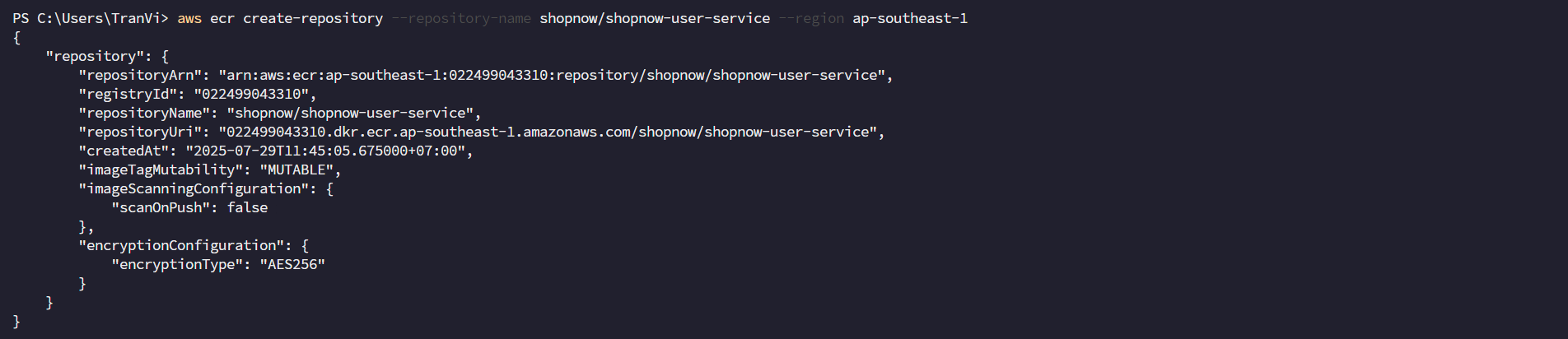
Create ECR Repository using AWS CLI
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name shopnow/shopnow-frontend --region ap-southeast-1
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name shopnow/shopnow-config-server --region ap-southeast-1
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name shopnow/shopnow-discovery-server --region ap-southeast-1
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name shopnow/shopnow-product-service --region ap-southeast-1
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name shopnow/shopnow-user-service --region ap-southeast-1
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name shopnow/shopnow-shopping-cart-service --region ap-southeast-1
After successful creation, you will get the following result:
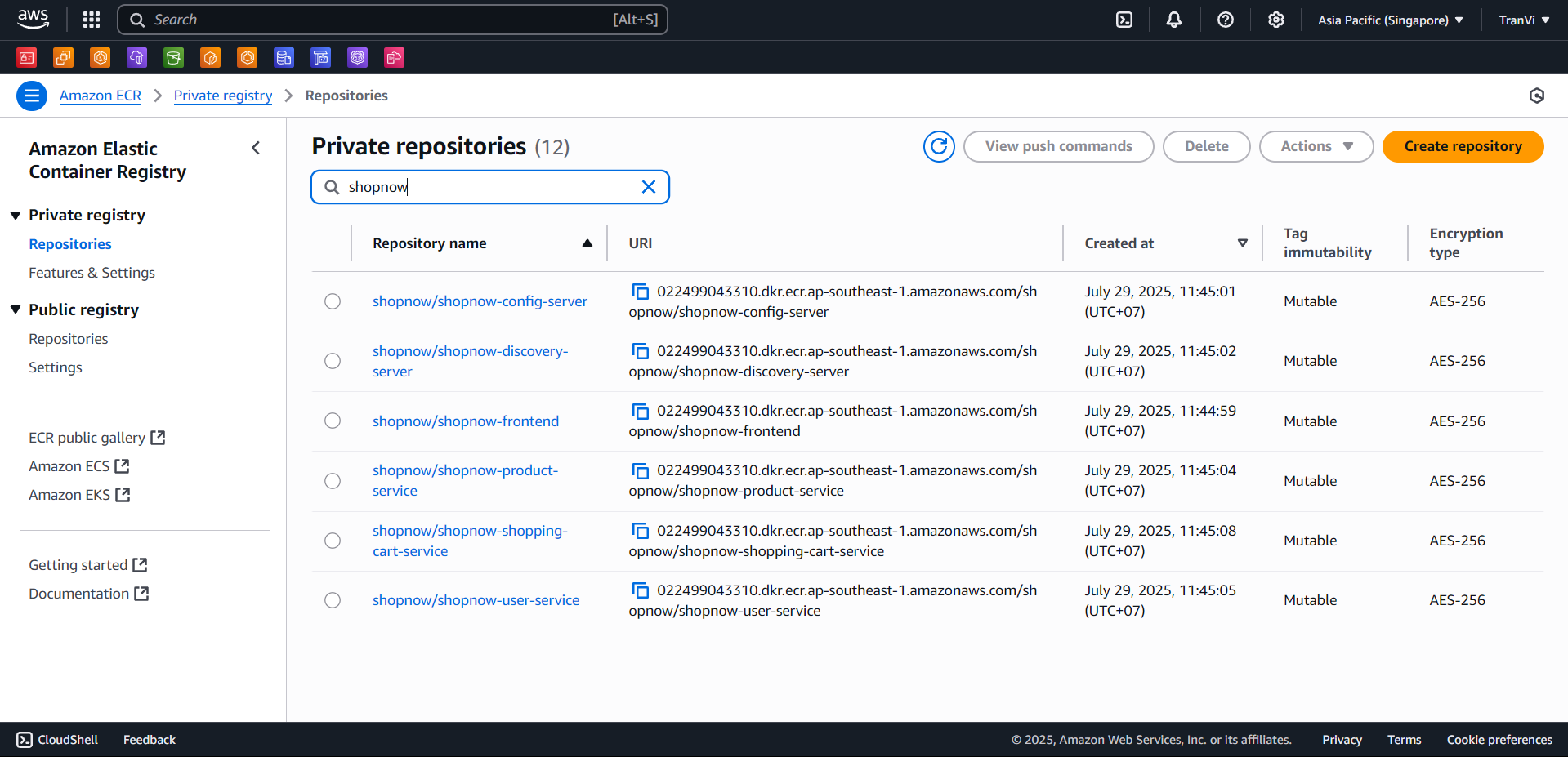
EKS Cluster
Next, we will create EKS Cluster using eksctl.
eksctl create cluster --name workshop-2-cluster --region ap-southeast-1 --without-nodegroup
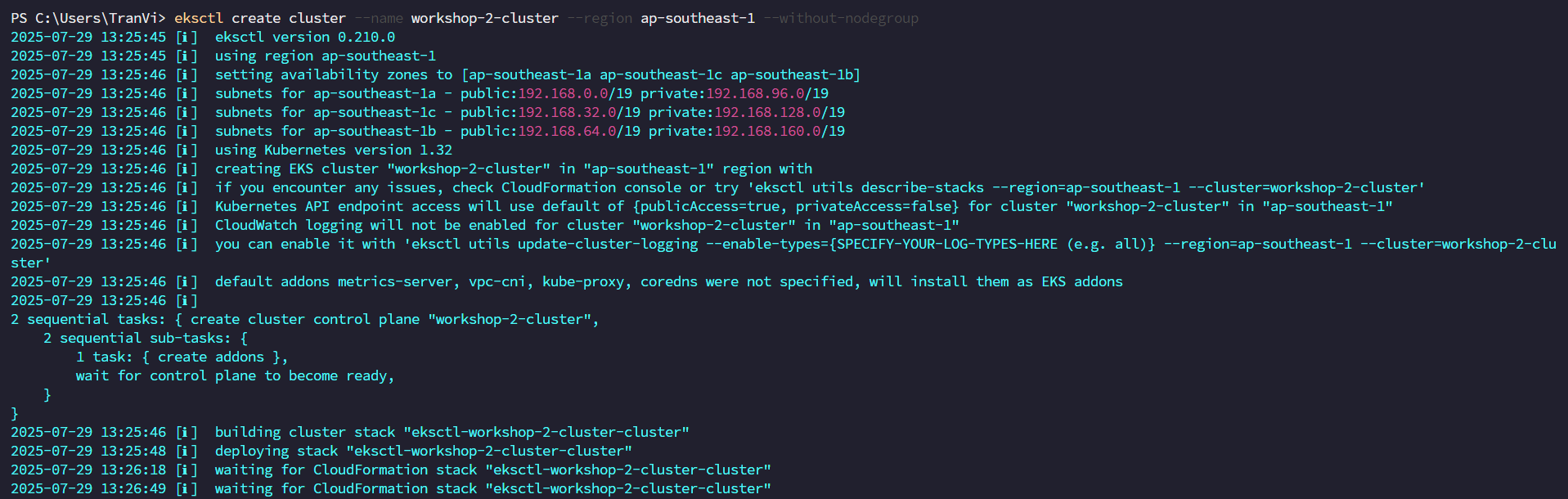
eksctl will proceed to create a CloudFormation Stack to create the EKS Cluster.
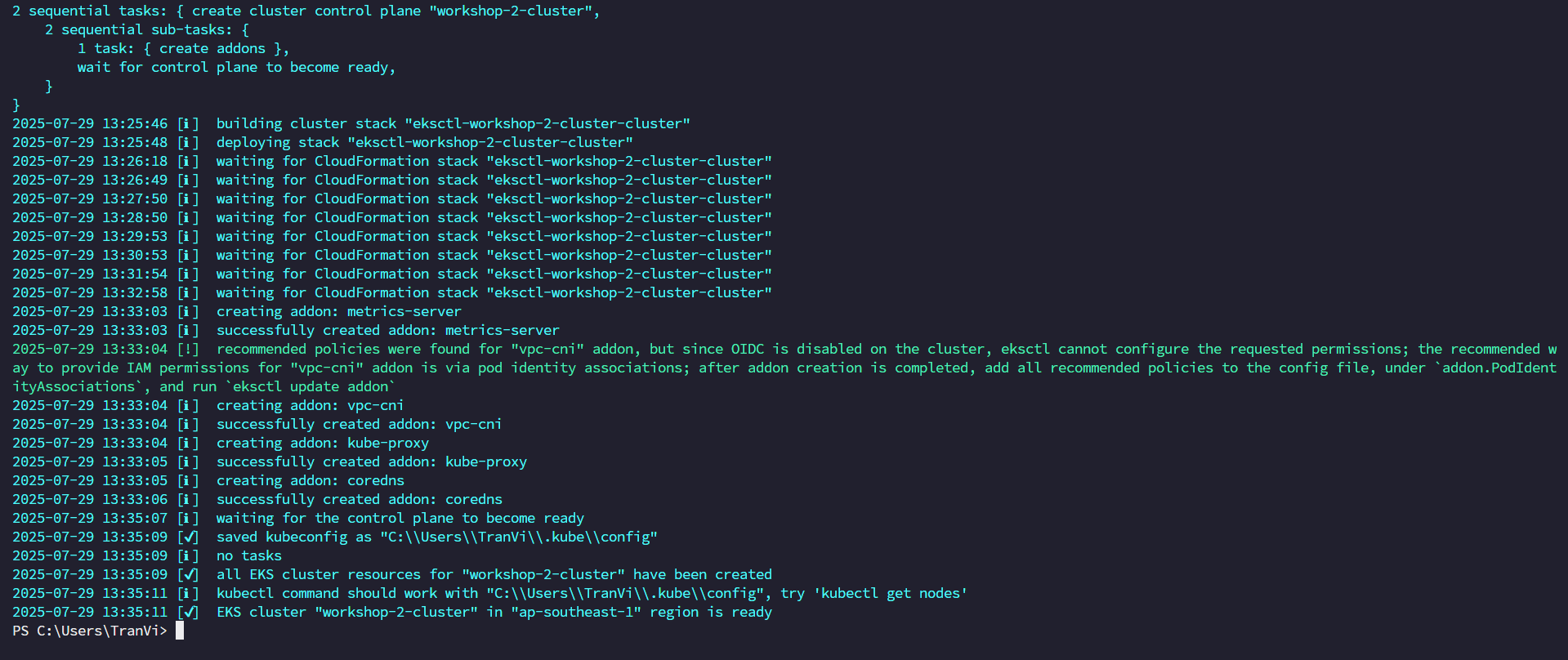
To be able to access the EKS Cluster, we need to update kubeconfig.
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name workshop-2-cluster --region ap-southeast-1

kubectl config get-contexts
kubectl cluster-info
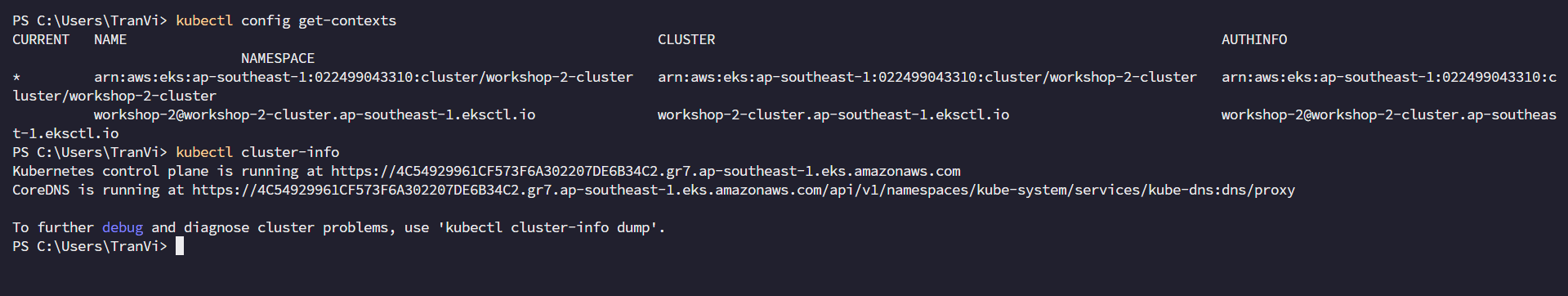
kubectl get nodes

Here we see the Cluster doesn’t have nodes yet, we will create node group using eksctl. Besides creating node group using eksctl cli, we can configure a yaml file to create node group ensuring it’s more visual.
eksctl create nodegroup \
--cluster=workshop-2-cluster \
--region=ap-southeast-1 \
--name=workshop-2-node-group \
--node-type=t3.large \
--nodes=2 \
--nodes-min=1 \
--nodes-max=4 \
--node-volume-size=20 \
--node-volume-type=gp3 \
--node-private-networking \
--managed \
--enable-ssm \
--ssh-access=false
Configure yaml file to create node group.
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: workshop-2-cluster
region: ap-southeast-1
version: "1.32"
vpc:
cidr: "192.168.0.0/16"
nat:
gateway: Single
managedNodeGroups:
- name: workshop-2-node-group
instanceType: t3.large
desiredCapacity: 3
minSize: 3
maxSize: 6
volumeSize: 20
volumeType: gp3
volumeIOPS: 3000
volumeThroughput: 125
volumeEncrypted: true
privateNetworking: true
availabilityZones: ["ap-southeast-1a", "ap-southeast-1b", "ap-southeast-1c"]
ssh:
allow: false
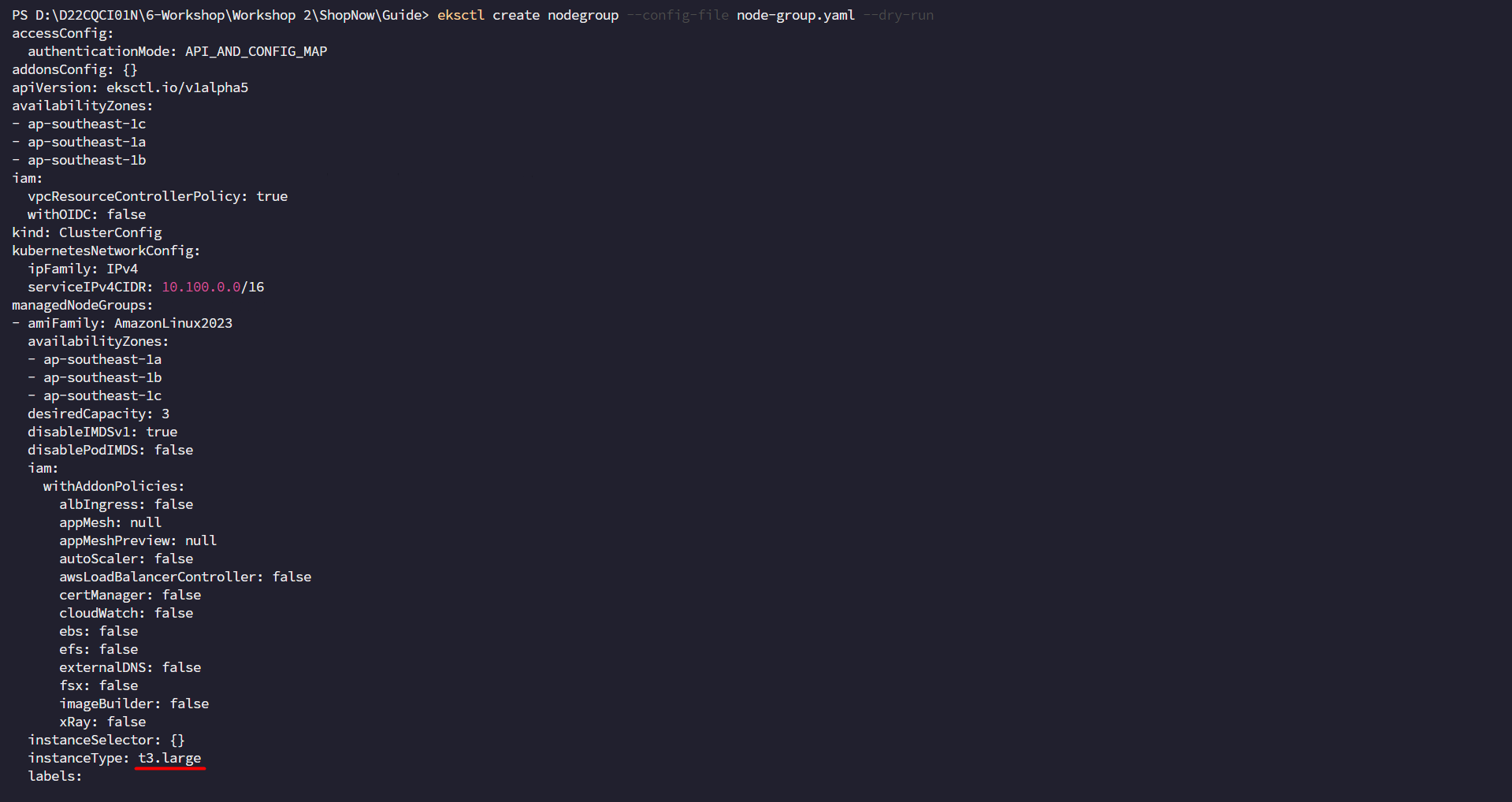
Check if the yaml configuration file has been created successfully or not.
eksctl create nodegroup --config-file node-group.yaml --dry-run
Proceed to apply the yaml configuration file.
eksctl create nodegroup --config-file node-group.yaml
Similar to creating the Cluster, eksctl also proceeds to create a CloudFormation Stack to create the node group.
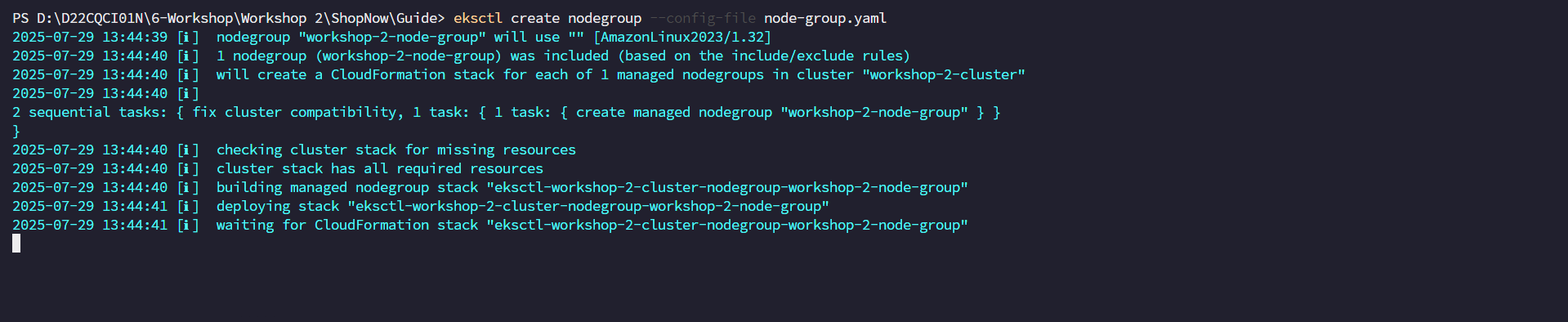
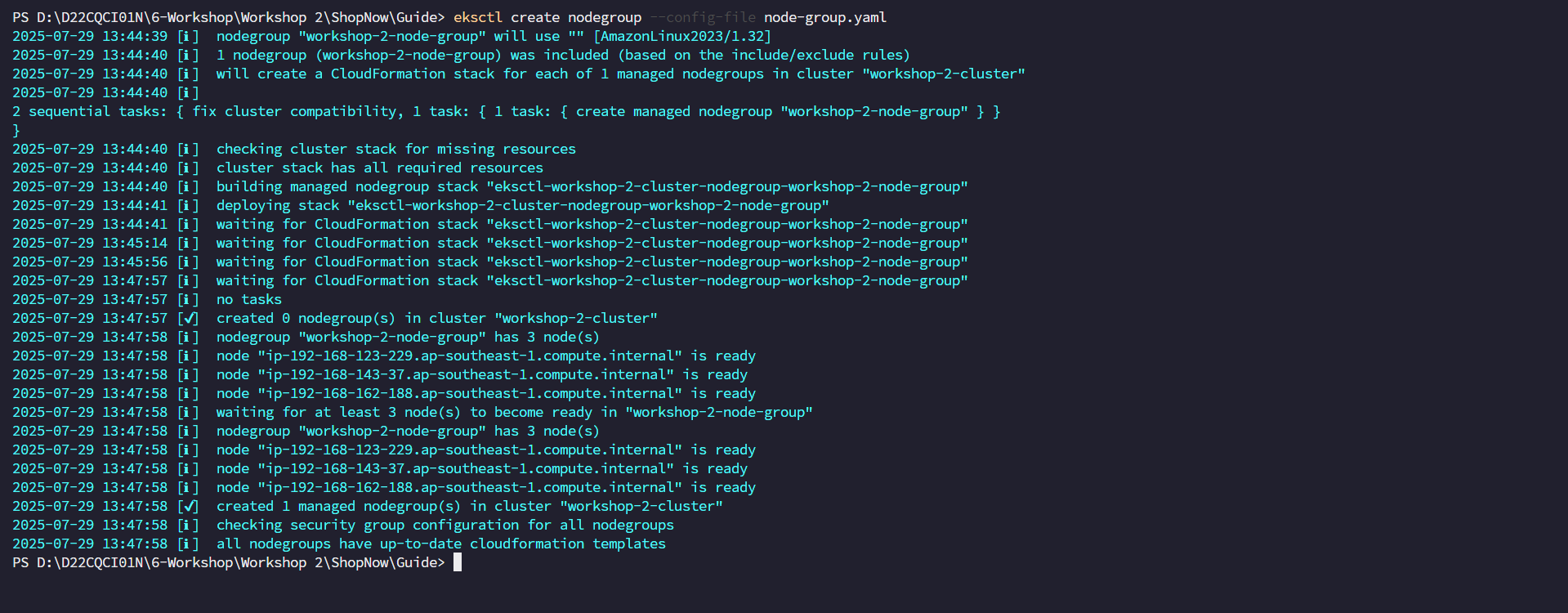
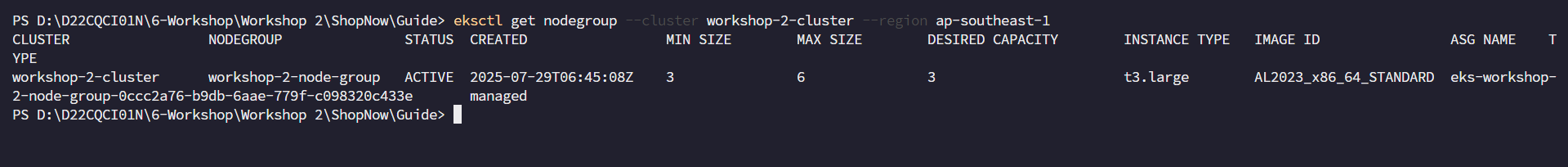
Check if the node group has been created successfully or not.
eksctl get nodegroup --cluster workshop-2-cluster --region ap-southeast-1
kubectl get nodes
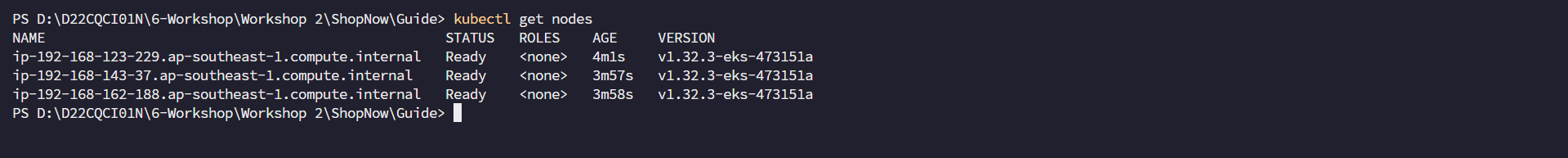
Thus we have successfully created the EKS Cluster and the nodes have been initialized successfully.